Evolution Of Intel Processor
Sandy Bridge processors are a very remarkable evolution on the previous Nehalem and Westmere, with a number of changes at a technical level but maintaining its name: Intel Core i3, i5 and i7, being low, medium and high range respectively.
The 4004 CPU was the forerunner of all of today’s Intel offerings and, to date, all PC processors have been based on the original Intel designs. The first chip used in an IBM PC was Intel’s 8088. This was not, at the time it was chosen, the best available CPU, in fact Intel’s own 8086 was more powerful and had been released earlier. The 8088 was chosen for reasons of economics: its 8-bit data bus required less costly motherboards than the 16-bit 8086.

Also, at the time that the original PC was designed, most of the interface chips available were intended for use in 8-bit designs. These early processors would have nowhere near sufficient power to run today’s software.
- Intel’s founding traces back through Fairchild Semiconductor to Shockley Semiconductor Lab, the post-Bell Labs home of transistor co-inventor William Shockley. Founded in 1955 5, Shockley Labs focused on the development and evolution of the transistor. However, in 1957.
- More than 30 years later, or roughly 3,000 calendar years in computer time, x86 continues to evolve (see how easy it is for creationism and evolution to co-exist?) from its modest start in 1978.
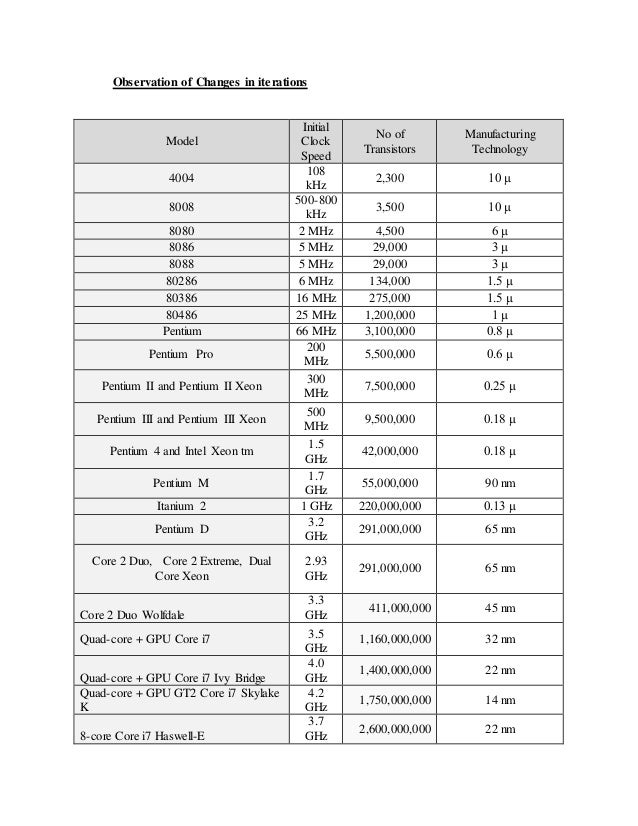
The table below shows the generations of processors from Intel’s first generation 8088/86 in the late 1970s to the eighth-generation AMD Athlon 64, launched in the autumn of 2003:
Chronological Evolution of CPUs
| Type/ Generation | Year | Data/ Address bus width | Level 1 Cache (KB) | Memory bus speed (MHz) | Internal clock speed (MHz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8088/ First | 1979 | 8/20 bit | None | 4.77-8 | 4.77-8 |
| 8086/ First | 1978 | 16/20 bit | None | 4.77-8 | 4.77-8 |
| 80286/ Second | 1982 | 16/24 bit | None | 6-20 | 6-20 |
| 80386DX/ Third | 1985 | 32/32 bit | None | 16-33 | 16-33 |
| 80386SX/ Third | 1988 | 16/32 bit | 8 | 16-33 | 16-33 |
| 80486DX/ Fourth | 1989 | 32/32 bit | 8 | 25-50 | 25-50 |
| 80486SX/ Fourth | 1989 | 32/32 bit | 8 | 25-50 | 25-50 |
| 80486DX2/ Fourth | 1992 | 32/32 bit | 8 | 25-40 | 50-80 |
| 80486DX4/ Fourth | 1994 | 32/32 bit | 8+8 | 25-40 | 75-120 |
| Pentium/ Fifth | 1993 | 64/32 bit | 8+8 | 60-66 | 60-200 |
| MMX/ Fifth | 1997 | 64/32 bit | 16+16 | 66 | 166-233 |
| Pentium Pro/ Sixth | 1995 | 64/32 bit | 8+8 | 66 | 150-200 |
| Pentium II/ Sixth | 1997 | 64/32 bit | 16+16 | 66 | 233-300 |
| Pentium II/ Sixth | 1998 | 64/32 bit | 16+16 | 66/100 | 300-450 |
| Pentium III/ Sixth | 1999 | 64/32 bit | 16+16 | 100 | 450-1.2GHz |
| AMD Athlon/ Seventh | 1999 | 64/32 bit | 64+64 | 266 | 500-2.2GHz |
| Pentium 4/ Seventh | 2000 | 64/32 bit | 12+8 | 400 | 1.4GHz-3.6GHz |
| AMD Athlon 64/ Eighth | 2003 | 64/64 bit | 64+64 | 400 | 2GHz-2.4GHz |
Intel is the masterpiece in computer processor world. Intel Corporation founded on 18 July 1968. The most successful processors from Intel since 1993 are listed with rare unseen pictures. I do collected interesting unknown information about each processor. Hope you enjoy this post.
Original Pentium Processors
Year of release: 1993
CPU speed: 66MHz, 75MHz, 90MHz, 100MH up to 200MHz.
Socket: 273 pin PGA (Pin Grid Array)
Manufacturing technology: 0.8µ
Remarks: In 1993 this is the first processor capable of executing 112 million commands per second. This made easy for computers to process real world data such as sound, speech and photo images.
Pentium Pro Processors
Year of release: 1995
CPU speed: 166MHz, 180MHz and 200MHz
Socket: 387 pin PGA (Pin Grid Array)
Manufacturing technology: 0.6µ
Remarks: Primarily used for servers
Pentium MMX Processor
Year of release: 1997
CPU speed: 233, 266, 300, 333, 450 MHz
Evolution Of Intel Processors Pdf
Manufacturing technology: 0.35µ
Socket: 296/321 pin PGA processor package.
Remarks: Support Intel MMX technology.
Celeron (Pentium II based) Processor
Year of release: 1998
CPU speed: 266, 300 MHz
Manufacturing technology: 0.25µ
Socket: 242 pin slot 1 single edge processor package (SEPP)
Pentium III and Pentium III Xeon Processor
Year of release: 1999
CPU speed: 500, 533, 600, 733, 800 MHz
Manufacturing technology: 0.18µ
Socket: 242 pin slot 1 single edge contact cartridge 2 (SECC2)
Remarks: Improved version of PII processor. Supports Streaming SIMD Extensions (SSE) instruction set. SSE is the extension to x86 architecture. Introduced low power consumption in idle state technology.
Pentium 4 Processor
Year of release: 2000
CPU speed: 1.5, 1.6, 1.8, 2.0, 2.4 GHz
Manufacturing technology: 0.18µ
Socket: PGA 478, PGA 423 (Pin Grid Array)
Remarks: Used in desktop and entry level workstation systems
Intel Xeon Processor
Year of release: 2001
CPU speed: 1.4, 1.5, 1.7 and up to 3.6 GHz
Manufacturing technology: 0.18µ
Socket: OLGA 603 (Organic Land Grid Array)
Remarks: Used in high performance servers & workstations. Named as “Xeon” (not “Pentium Xeon”).
Intel Pentium M Processor
Year of release: 2003
CPU speed: 1.7, 1.8, 2.0 and up to 2.26 GHz
Manufacturing technology: 0.09µ (90nm) uses Nano technology
Socket: Micro-FCPGA and Micro-FCBGA (Flip-chip Ball Grid Array)
Remarks: Intel Centrino technology used. Intel Pro/wireless and network connection are the components of Centrino technology. Centrino technology specifically designed for portable computer such as Laptop.
Micro-FCBGA
Micro-FCPGA
Intel Itanium 2 Processor (Single core)
Year of release: 2002
CPU speed: 1 GHz up to 1.6 GHz
Manufacturing technology: 0.13µ
Evolution Of Intel Processors Ppt
Socket: PAC611 (Pin Array Cartridge)
Remarks: New instruction set. Architecture is based on Explicitly Parallel Instruction Computing (EPIC). Designed for high end enterprise-class servers.
Intel Pentium D processor
Year of release: 2005
CPU speed: 2.6 and up to 3.2 GHz
Manufacturing technology: 0.065µ (65nm)
Socket: LGA 775 (Land Grid Array) also known as “socket T”

Remarks: Dual core technology introduced. First desktop dual core processor. Each core runs at same speed.

Intel Core 2 Duo and Dual-core Xeon Processor
Year of release: 2006
CPU speed: 1.8 and up to 2.93 GHz
History Of Intel Processors Timeline
Manufacturing technology: 0.065µ (65nm)
Socket: LGA 775 (Land Grid Array) also known as “socket T”
Remarks: Desktop and server processors with dual cores. Hyper threading, Intel VT-x, multiple OS support, SSSE3 SIMD instructions and Intel TXT (Trusted Execution Technology).
Intel Itanium 2 Processor 9000 series (Dual core)
Year of release: 2006
CPU speed: 1.6 GHz
Manufacturing technology: 0.09µ (90nm)
Socket: FC-LGA6 (LGA1248)
Remarks: Itanium processor with two cores. Performance has been doubled compare to previous version.
Quad core Intel Processors
Year of release: 2006 (Quad core Intel Core 2 Extreme and Quad core Intel Xeon Processors)

Year of release: 2007 (Core 2 Quad processor)
CPU speed: 2.66 GHz up to 3.2 GHz
Manufacturing technology: 65nm and 45nm
Socket: LGA 775 (Land Grid Array)
Remarks: 64 bit microarchitecture. These quad core processors were delivered fifty percent higher performance compare to dual core processors. New SSE4 instruction set for improved video, imaging and 3D content.
Intel Core i7 Processors
Year of release: 2008
CPU speed: 2.66GHz up to 3.20GHz (Turbo boost)
Manufacturing technology: 45nm
Socket: LGA1366
Remarks: 3-channel DDR3 RAM support. Integrated HD GPU. 4 physical cores. Front side bus replaced with QuickPath.
Intel Core i5 Processors
Year of release: 2009
CPU speed: 2.40GHz up to 3.60GHz (Hyper-Threading Turbo boost)
Manufacturing technology: 32nm
Socket: LGA1156
Remarks: 2-channel DDR3 RAM support. Integrated HD GPU. 4 physical cores.
Intel Core i3 Processor
Year of release: Jan, 2010
CPU speed: 2.93GHz up to 3.33GHz
Manufacturing technology: 32nm
Socket: LGA1156
Remarks: 2-channel DDR3 RAM support. Integrated HD GPU. 2 physical cores and 4 threads.
Intel Pentium Processors
Year of release: Jan, 2010
CPU speed: 2.8GHz and 2.93GHz
Manufacturing technology: 32nm
Socket: LGA1156
Remarks: 2-channel DDR3 RAM support. Integrated HD GPU. 2 physical cores and 4 threads.